Spatial Computing's Role in Shaping Tomorrow
Spatial computing, the amalgamation of physical and digital worlds, is emerging as a transformative force in the realm of technology. This groundbreaking concept transcends traditional computing paradigms, introducing a new era where the digital experience seamlessly integrates with our physical surroundings. In this exploration of spatial computing, we delve into its core principles, applications, and the profound impact it has on shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
Spatial Computing and the Future:
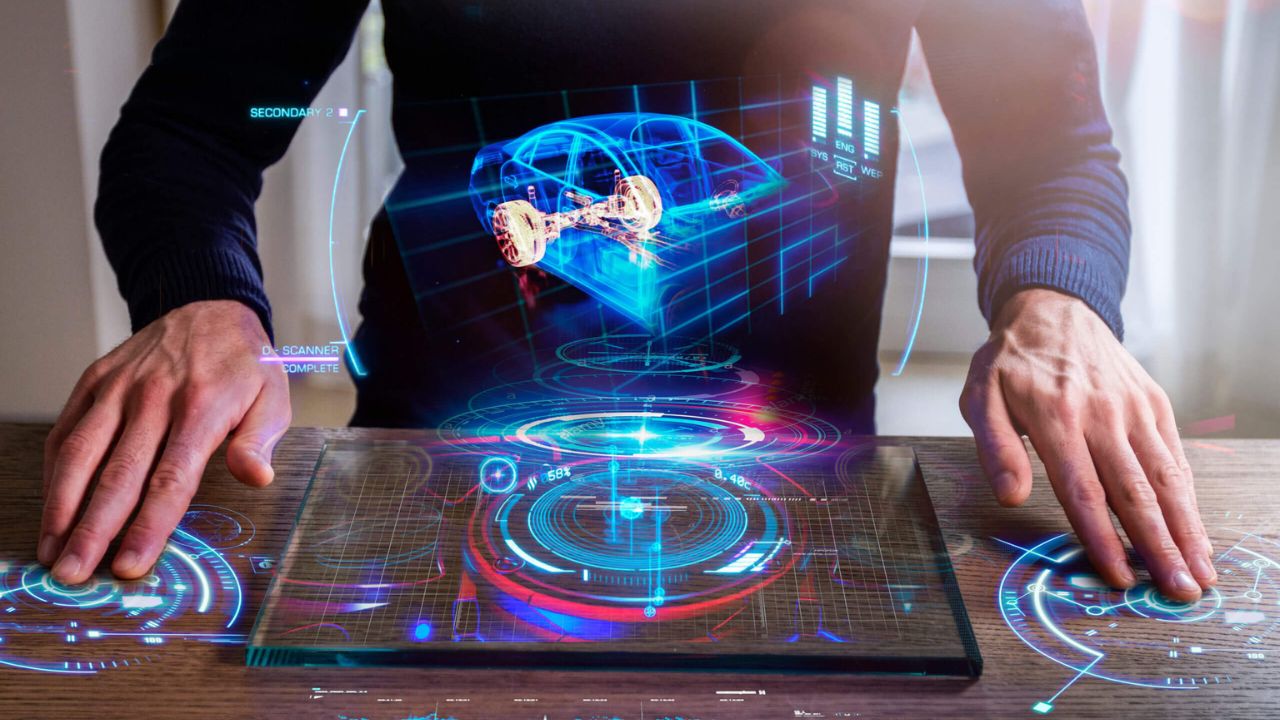
Spatial computing is the convergence of the physical and digital domains, seamlessly blending digital information with the real-world environment. This innovative technology extends beyond conventional interfaces, incorporating elements such as spatial awareness, computer vision, and augmented reality to craft immersive and interactive experiences. Essentially, spatial computing revolutionizes our perception and interaction with the surroundings by effectively merging the tangible and digital realms. XREAL, a trailblazer in spatial computing, pioneers the utilization of space and context in the digital realm, empowering computers to comprehend and interact with the physical world in real time.
Immersive Experiences in Virtual and Augmented Reality:
At the heart of spatial computing lies the capability to deliver immersive experiences through virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). VR transports users to entirely virtual environments, while AR overlays digital information onto the real world. From gaming and education to healthcare and design, spatial computing reshapes how we engage with content, making it more interactive and dynamic.
Enhancing Productivity in the Workplace:
Spatial computing has the potential to revolutionize the workplace by introducing novel ways of collaboration and productivity. Virtual meeting spaces, collaborative design environments, and data visualization in 3D space redefine how teams interact and innovate. This can lead to more efficient workflows and enhanced problem-solving, breaking down geographical barriers in a globally connected world.
Spatial Awareness in Healthcare:
The healthcare industry stands to benefit significantly from spatial computing. Surgeons can use AR to visualize patient data during procedures, medical professionals can explore 3D models of organs, and patients can engage in immersive therapy sessions. Spatial computing facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of medical information, leading to improved diagnostics and treatment strategies.
Education Revolutionized:
Spatial computing transforms education by providing immersive learning experiences. Students can explore historical events, dissect virtual organisms, and conduct experiments in a simulated environment. This hands-on, interactive approach enhances comprehension and retention, making learning more engaging and effective.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
While spatial computing presents immense possibilities, it also raises ethical considerations. Issues related to privacy, security, and the potential misuse of immersive technologies need careful examination. Striking a balance between innovation and responsible use is crucial to ensuring the positive impact of spatial computing.
Conclusion:
Spatial computing stands at the forefront of technological evolution, promising a future where our interactions with digital content are seamless, immersive, and deeply integrated into our physical reality. From revolutionizing industries to redefining education and healthcare, the applications of spatial computing are vast and varied. In charting our course through this digital frontier, it becomes crucial to responsibly embrace innovation, contemplating the ethical considerations and ensuring that spatial computing, led by XREAL, enhances our lives without compromising privacy and security. The expedition into spatial computing signifies more than just a technological leap; it marks a stride toward a more interconnected, intelligent, and enriching digital future.